Details of the Drug
General Information of Drug (ID: DMY18XK)
| Drug Name |
Penicillin G Sodium
|
||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Synonyms |
Penicillin G sodium salt; 69-57-8; Benzylpenicillin sodium; Crystapen; American penicillin; Pencillin G sodium; Sodium penicillin G; BENZYLPENICILLIN SODIUM SALT; Sodium penicillin; Sodium benzylpenicillinate; Sodium penicillin II; Veticillin; Penilaryn; Mycofarm; Novocillin; Sodium benzylpenicillin; Kesso-Pen; Pen-A-Brasive; Sodium benzylpenicillin G; Monosodium benzylpenicillin; Benzylpenicillinic acid sodium salt; Sugracillin sodium salt; Penicillin G Sodium, Crystalline; Sodium benzylp
|
||||||||||||||||||||||
| Indication |
|
||||||||||||||||||||||
| Therapeutic Class |
Antiinfective Agents
|
||||||||||||||||||||||
| Drug Type |
Small molecular drug
|
||||||||||||||||||||||
| Structure |
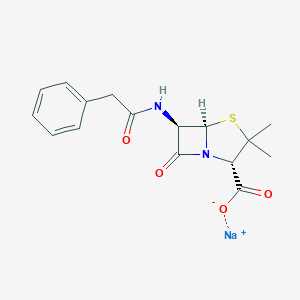 |
||||||||||||||||||||||
| 3D MOL is unavailable | 2D MOL | ||||||||||||||||||||||
| #Ro5 Violations (Lipinski): 0 |
Molecular Weight | 356.4 | |||||||||||||||||||||
| Logarithm of the Partition Coefficient | Not Available | ||||||||||||||||||||||
| Rotatable Bond Count | 4 | ||||||||||||||||||||||
| Hydrogen Bond Donor Count | 1 | ||||||||||||||||||||||
| Hydrogen Bond Acceptor Count | 5 | ||||||||||||||||||||||
| Chemical Identifiers |
|
||||||||||||||||||||||
| Cross-matching ID | |||||||||||||||||||||||
Molecular Interaction Atlas of This Drug
 Drug Therapeutic Target (DTT) |
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Molecular Interaction Atlas (MIA) | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||
